Kali Linux is a powerful and versatile operating system specifically designed for penetration testing, security auditing, and digital forensics. It comes preloaded with a wide array of specialized tools that make it an essential platform for cybersecurity professionals, ethical hackers, and security researchers.
While Kali Linux functions as a standard operating system, it’s the extensive suite of tools that truly sets it apart, offering everything you need for testing the security of networks, systems, and applications. When you first install Kali Linux, you can use it just like any other Linux distribution. However, to truly unlock its potential, you’ll need to dive into the diverse set of utilities it includes.
Kali comes equipped with hundreds of tools, many of which serve similar purposes. While it may seem overwhelming at first, you don’t need to master every single tool. In fact, many of the tools are alternatives to one another, designed to accomplish the same tasks in different ways.
The key to effectively using Kali is understanding the range of tools available, how they function, and selecting the right ones for your specific needs. Once you grasp which tools are most effective for each task, you’ll be able to focus on mastering those and applying them in real-world security assessments. In this guide, we’ll introduce you to Kali Linux and help you navigate its powerful features.
About Kali Linux
The most amazing feature of Kali Linux is its price – it is free to use. Despite being packed with tools, you don’t have to pay anything to download and use it. The secret behind this giveaway is that all of the components of the Kali package are individually free. The creators of Kali sought out useful free systems and packaged them together.
The main element in Kali is the Linux operating system. This is taken from Debian Linux. If you aren’t interested in penetration testing, then you probably should install Debian Linux instead of Kali because you will be using the same operating system.
Although Kali is given away for free, it is actually owned by a business. The system is a product of Offensive Security. This organization has created a number of open-source projects. All of those systems are free to use. The company makes its money by providing consultancy services. Essentially, Offensive Security is a cybersecurity business that created bundles of tools for its consultants and customers to use and made those bundles available to the world.
Many of the tools in the Kali bundle are also open-source projects. These are run by volunteers and many IT professionals and cybersecurity professionals contribute to the development of these systems for free. They get the prestige associated with these tools and that advances their careers, so there is a business logic behind getting involved in these projects and they attract very skilled and respected contributors.
Acquiring Kali Linux
Go to the website for the Kali project in order to find out more about Kali Linux. You can just go straight to the Kali Linux download page if you just want to get on with installing the system.
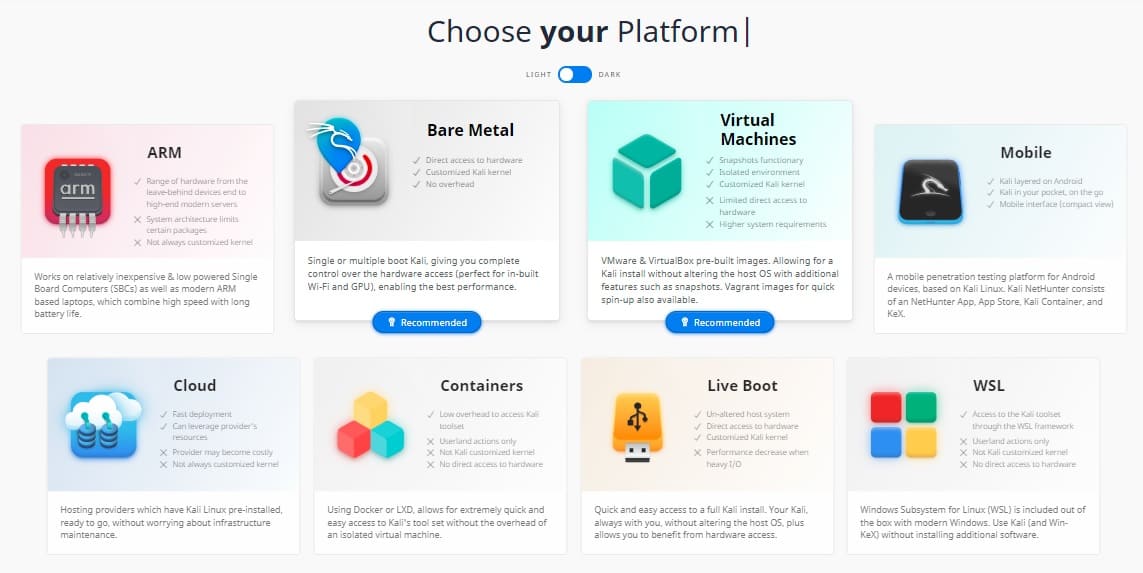
The service offers eight different installation options, including versions that can be run on Android devices, on VMs, and on containers. The most popular option is to install the software on a bare-metal computer.
Whichever installation option you choose, you will find an installation guide in the section that includes the download file.
Kali Linux tools
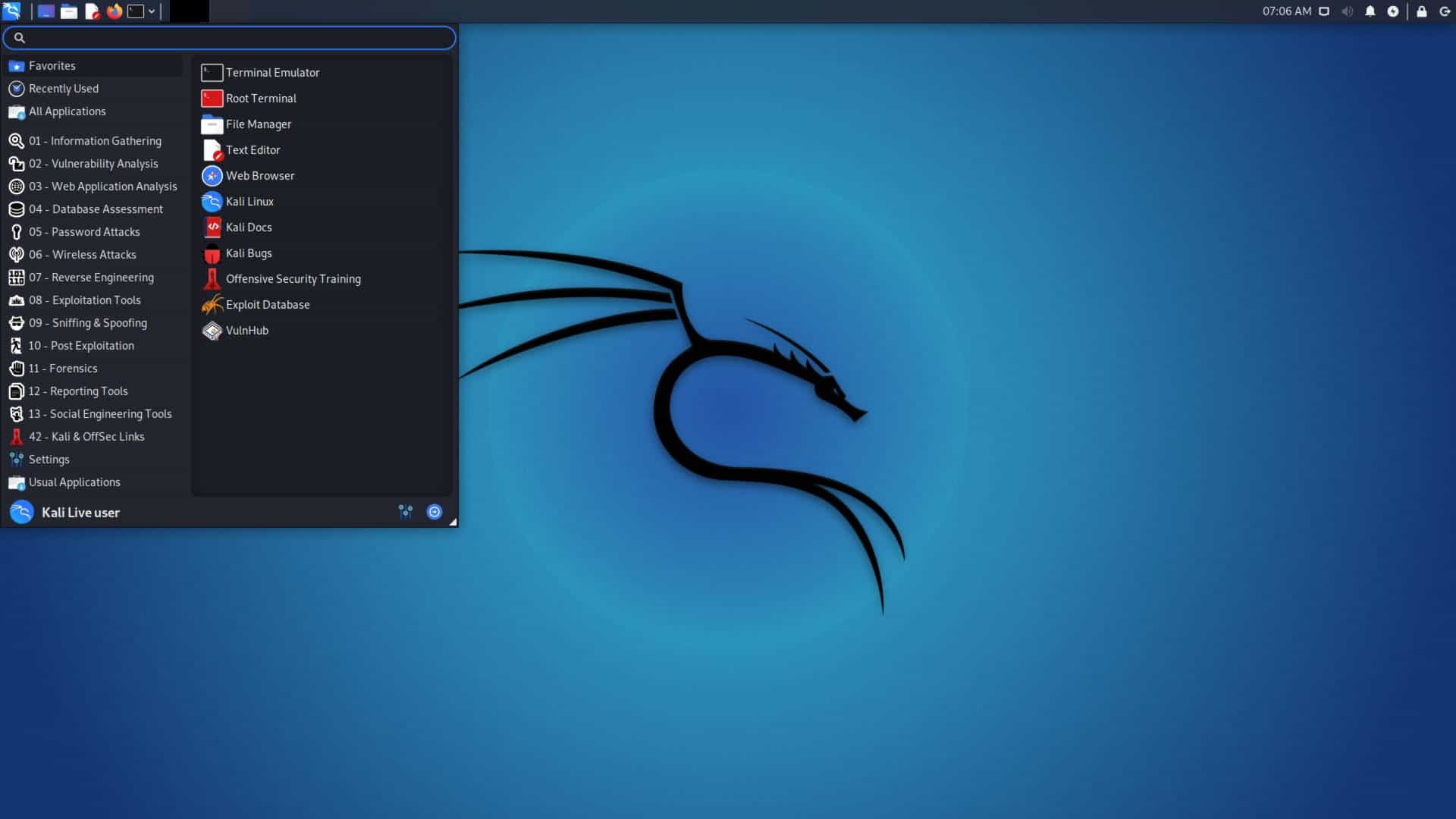
Kali Linux has a graphical user interface – you don’t have to work at the command line all of the time.
Not all of the tools included in the system work through the interface, though. Some of them are only available at the command line.
There are about 300 tools built into Kali Linux – in addition to the Debian operating system. All of the tools are focused on pen-testing. In this guide, we will look at just the 20 most significant tools that you can find within the Kali Linux package.
You can see a full list of the penetration testing tools in Kali Linux in our PDF.

Click on the image above to open the Kali Linux Cheat Sheet PDF in a new window. Each tool’s name is a link through a website that explains the functions of the utility.
The tools that we will look at in this guide are:
- Aircrack-ng A packet sniffer for wireless LANs.
- Autopsy A graphical interface to The Sleuth Kit, which aids forensic exploration of hard disks.
- Armitage A front end for Metasploit tools that manages attack strategies.
- Burp Suite A system that launches man-in-the-middle attacks and includes password cracking.
- BeEF The Browser Exploitation Framework tries to break into servers through websites.
- Cisco Global Exploiter Attacks Cisco routers and switches.
- Ettercap A traffic interceptor designed for man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Foremost A command-line disk copying and file recovery tool.
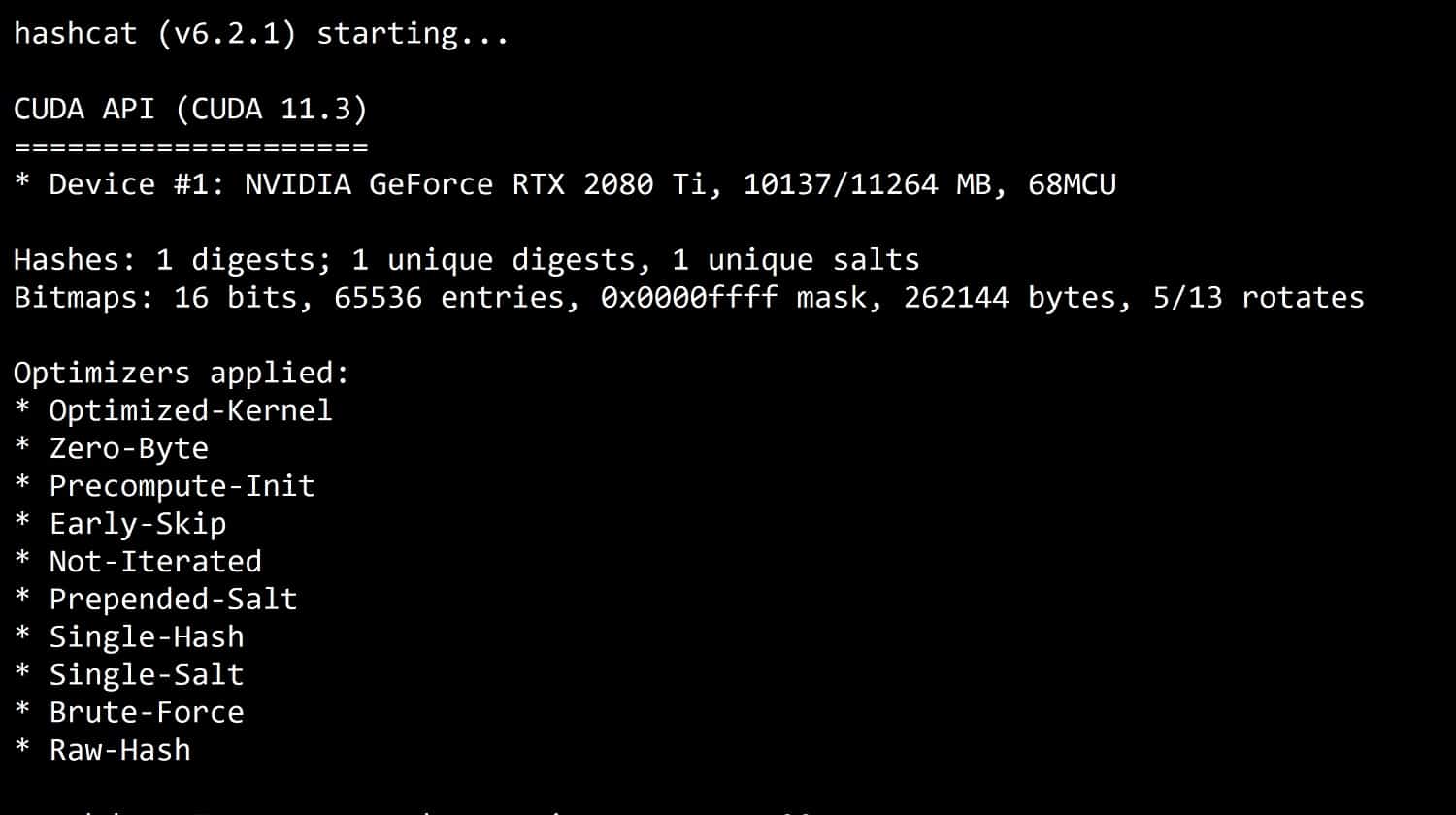
- Hashcat A password cracker.
- Hydra A password cracker.
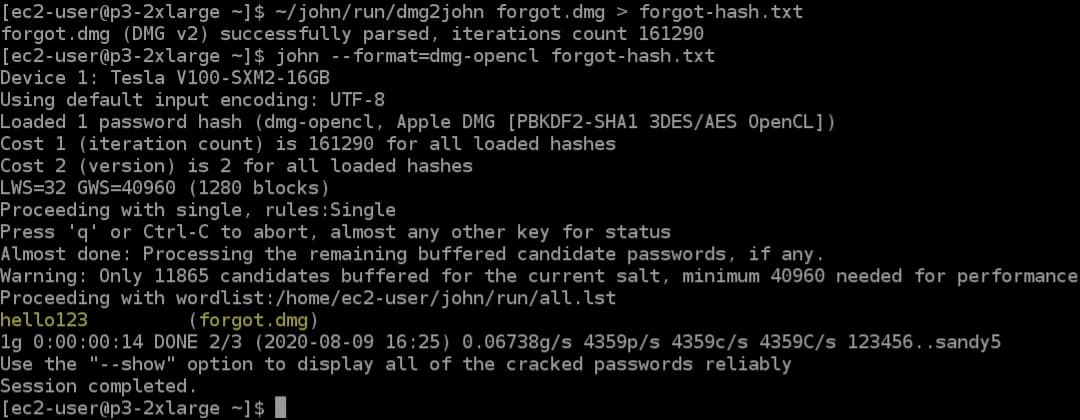
- John the Ripper A command-line password cracker.
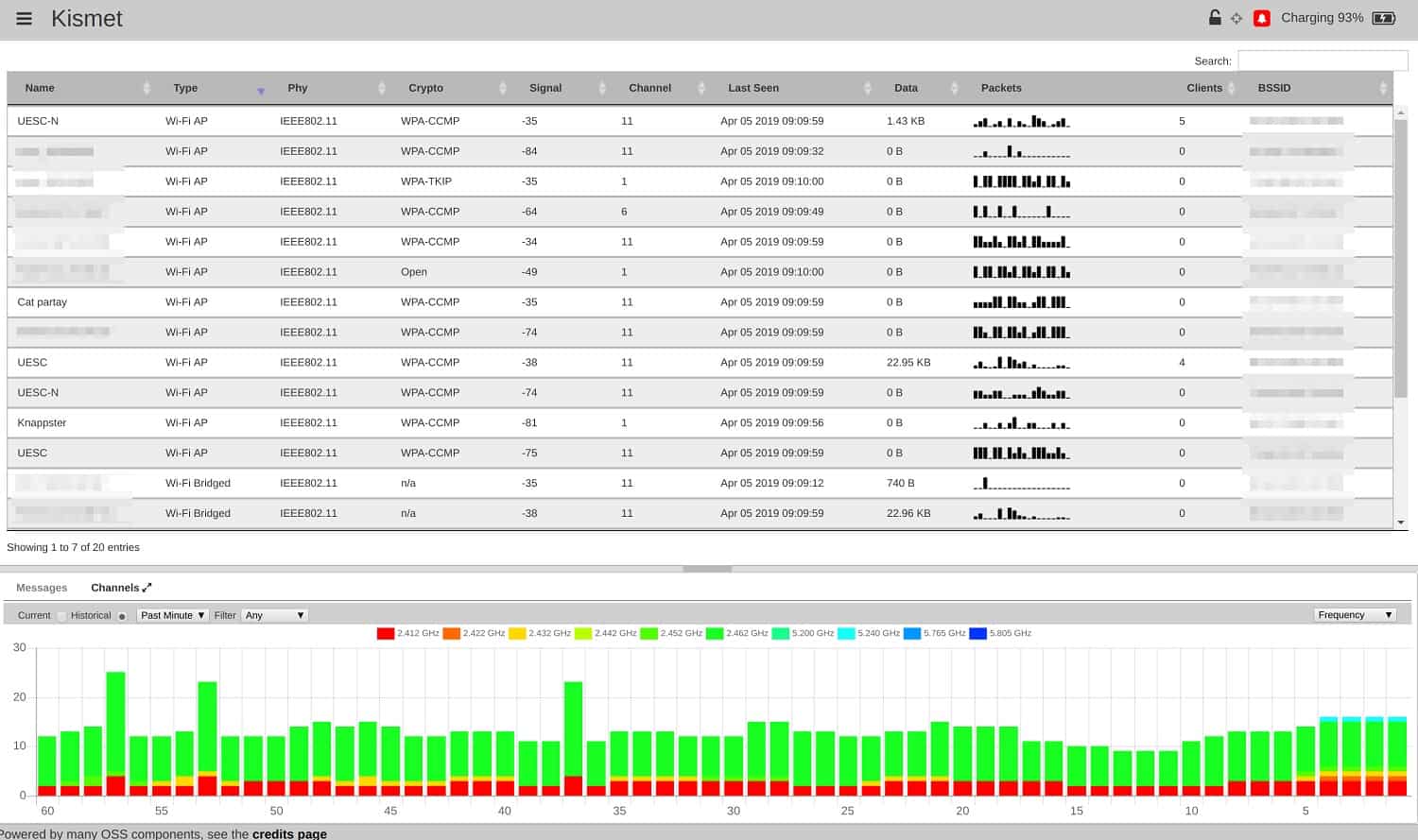
- Kismet A network scanner, packet sniffer, and intrusion detection system for wireless networks.
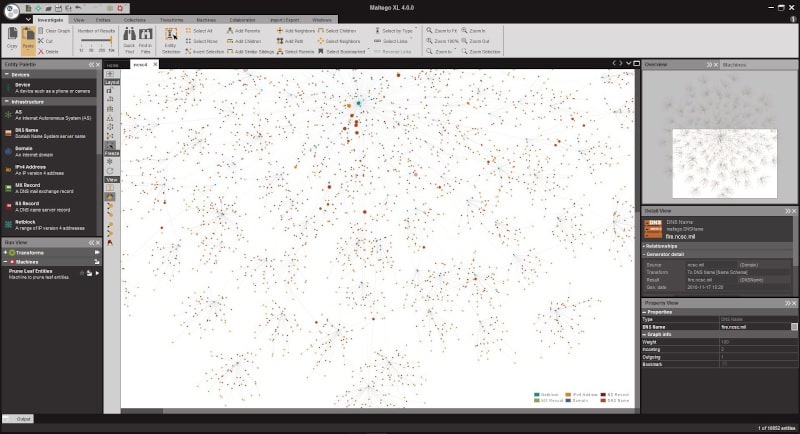
- Maltego A data discovery tool that maps relationships between data, including network layouts, social media connections, and software dependencies.
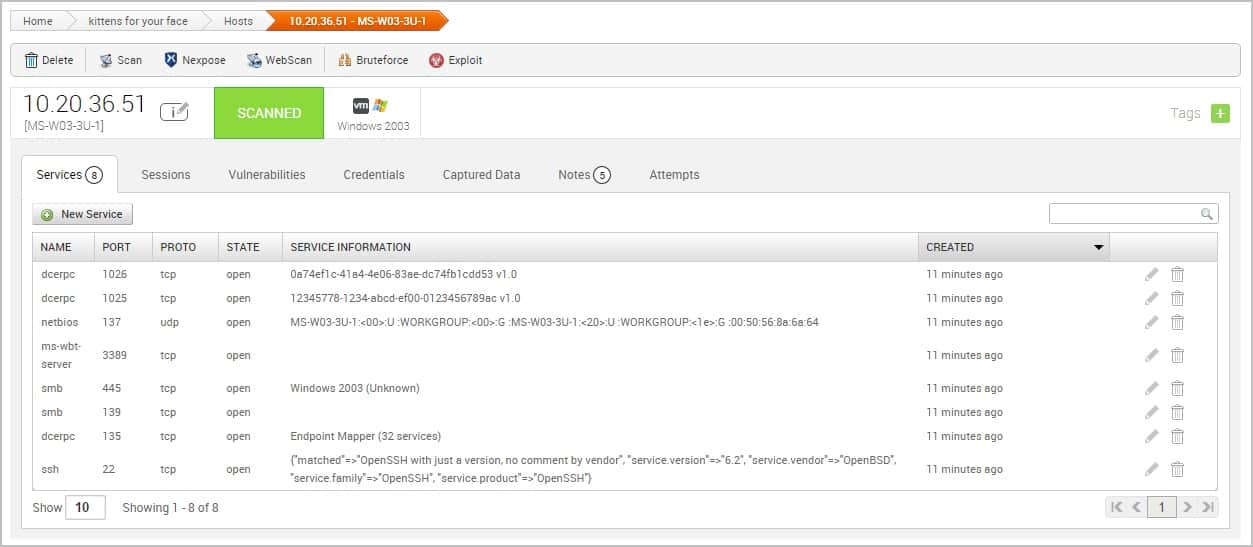
- Metasploit Framework Scans targets for endpoints and then builds attacks based on discovered knowledge.
- Nikto A command-line Web vulnerability scanner.
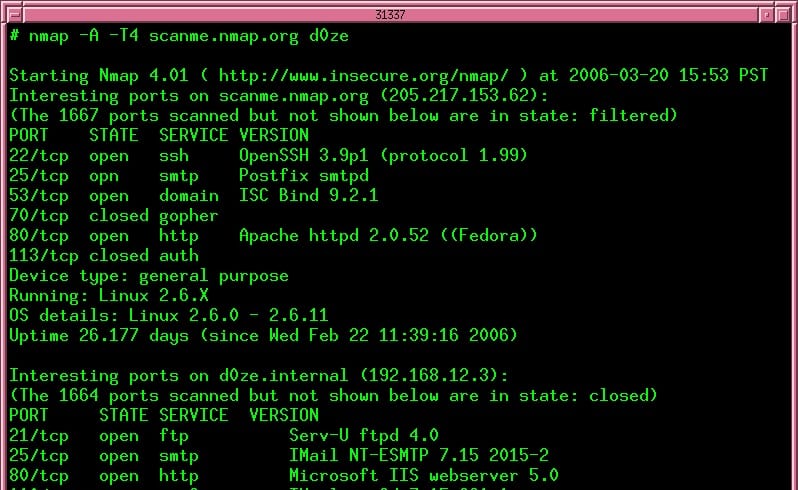
- Nmap A command-line network scanner and device discovery tool.
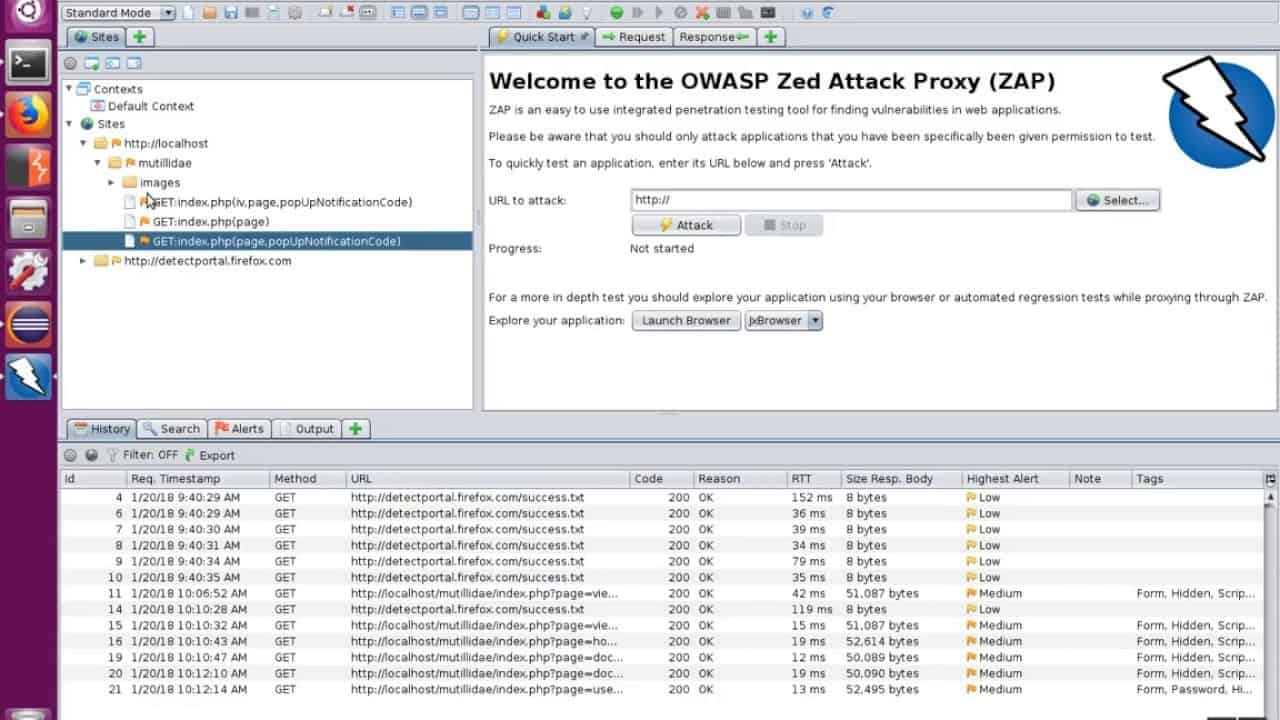
- OWASP ZAP The Zed Attack Proxy is a Web vulnerability scanner and traffic interceptor.
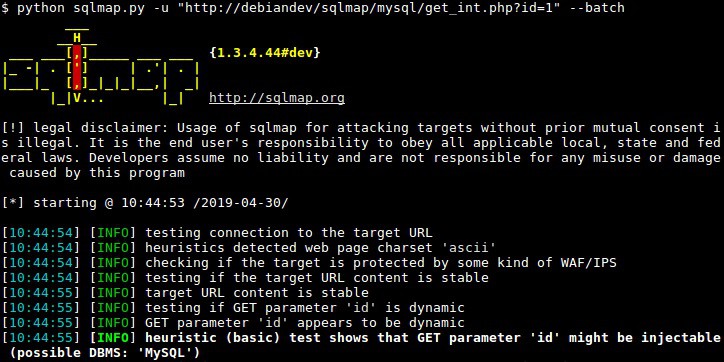
- sqlmap A command-line service for web vulnerability scanning and password cracking.
- Wireshark A world-famous packet sniffer.
- WPScan A vulnerability scanner for WordPress sites.
These are the most useful tools in the Kali bundle that you will probably use all the time when pen-testing. If you don’t want to bother installing the full Kali package that includes all of the other tools, you could just install Debian Linux and each of these tools individually because they are all available for free. The links in the tool names in the above list will take you through to the home page for that system.
You can read more about each of these tools in the following sections.
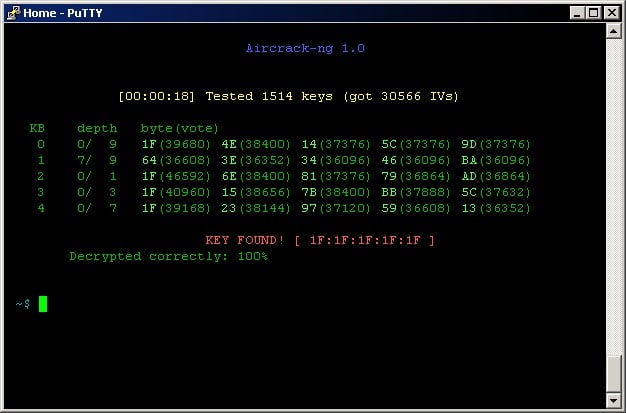
1. Aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng offers detection of wireless signals and it can extract data as it passes along a selected channel. The system allows you to export captured packets for analysis in another tool. The Aircrack-ng utility is a command-line system and it displays its output in multi-colored characters to aid data comprehension.
The Aircrack-ng features include the ability to crack passwords, but only on systems with weak security (WEP, WPA 1, WPA 2). It is also able to broadcast packets into a stream, which allows it to perform a variety of attacks. These include replay attacks, deauth injection, and man-in-the-middle attacks. It can also act as a fake AP.
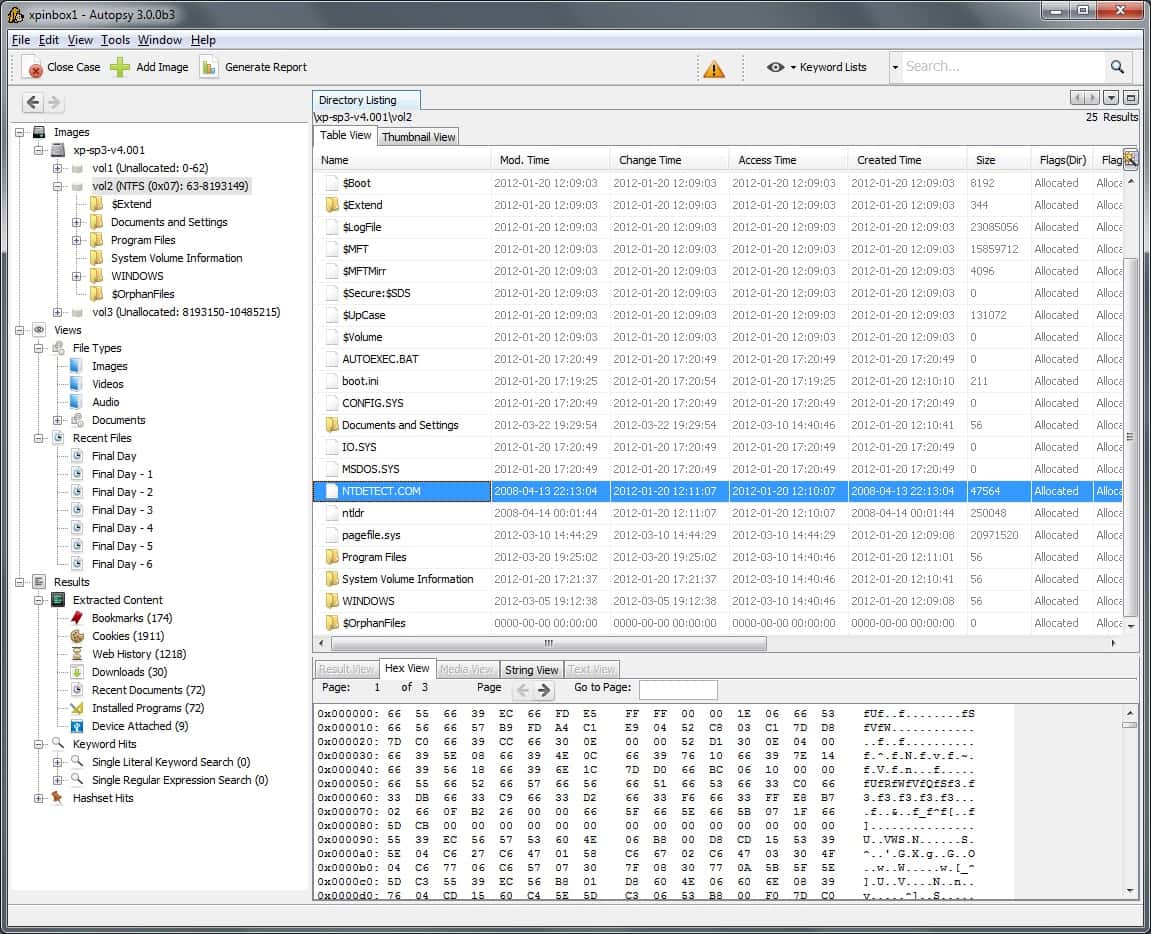
2. Autopsy
Autopsy operates as a graphical front end to The Sleuth Kit, which is also included in the Kali package. The Sleuth Kit is able to search down into a hard disk and recover files that have been deleted or possibly damaged by the loss of the File Access Table.
The combination of Autopsy and The Sleuth Kit is frequently used by law enforcement agencies to extract files from the confiscated devices of suspects. It is also able to extract images from phone memory cards.
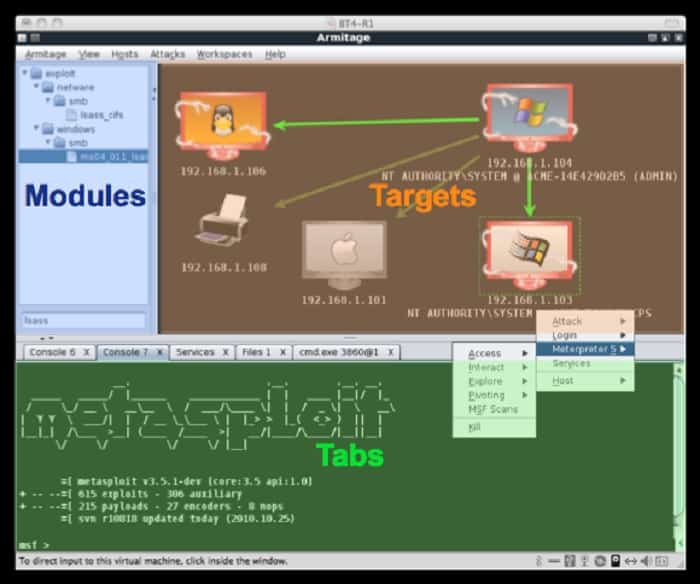
3. Armitage
Armitage is an attack manager that uses Metasploit as a back end. While the user is able to visualize discovered computers in Armitage, further commands in the interface get interpreted down to Metasploit, which implements further exploration.
As well as identifying devices and documenting their software and services, Armitage provides a collaboration platform for teams working on a pen testing project. It also enables an attack strategy to be formulated and then implemented through Metasploit.
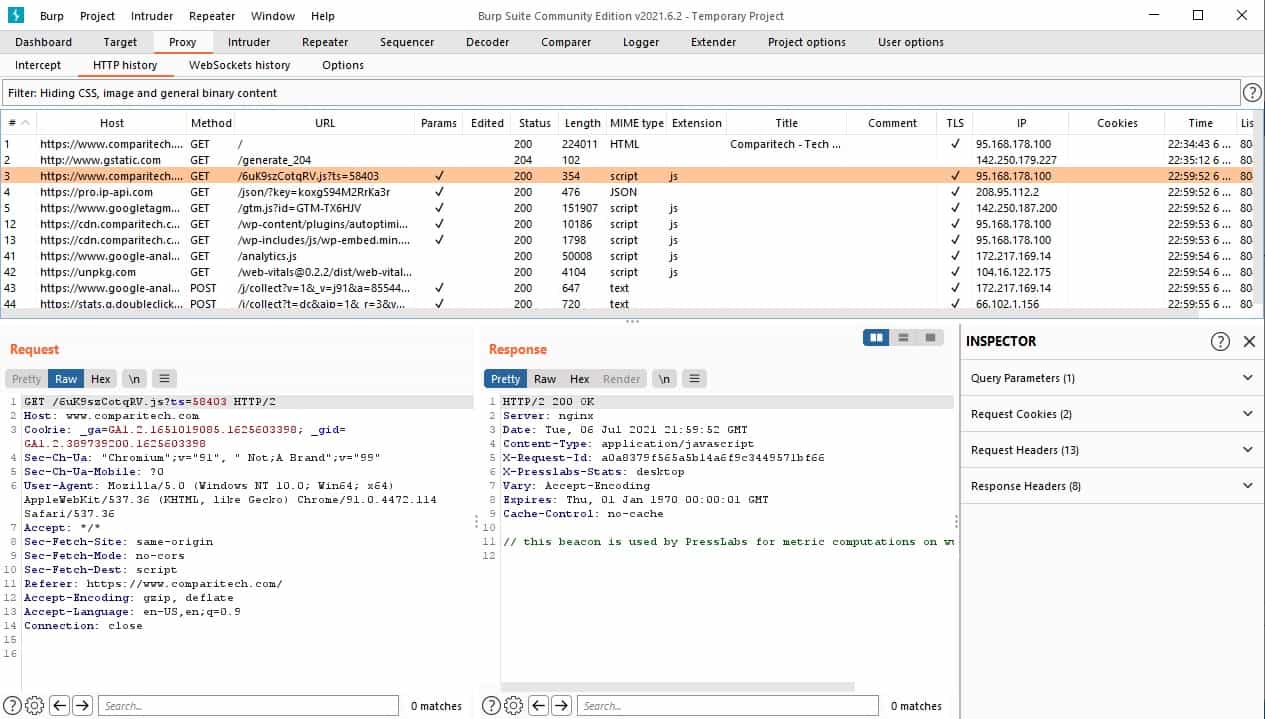
4. Burp Suite
Burp Suite is available in free and paid versions – you get the free Community Edition bundled in with Kali Linux. The Burp Suite version that comes with Kali is able to intercept the traffic that passes between a Web server and a Web browser to deliver and render a Web page.
It is possible to force the transaction onto HTTP to prevent the use of encryption. The unprotected data passing over the network can then be scanned for important information, such as login credentials. You can read more about Burp Suite and how to use it in our Burp Suite Cheat Sheet.
5. BeEF
BeEF stands for the Browser Exploitation Framework. It is a Web application pen testing tool that tests sites loaded into a test browser and scan for exploits. BeEF works at the command line and then triggers the opening of a browser to run the tests.
The system can be used to perform attack strategies that try to get into the supporting Web server through HTTP transactions.
6. Cisco Global Exploiter
The Cisco Global Exploiter is not a Cisco product; rather, it specializes in hacking Cisco-produced routers and switches. Cisco devices are very widely used, and they have their own operating system, called IOS. The Cisco Global Exploiter is a command-line utility that attempts to break into a device, using default and commonly-used passwords for the administrator account.
Sticking to a built-in knowledge of IOS, the Cisco Global Exploiter explores for known vulnerabilities with Cisco devices.
7. Ettercap
Ettercap is a packet capture tool that can facilitate a man-in-the-middle attack and also credentials capture. The system is available as a command-line utility and it also has a rudimentary graphical user interface.
The Ettercap system uses ARP poisoning to establish a position as a listener between a Web server and a browser. It lets the attacker diver traffic from an intended destination and it is also able to use the system to create a fake AP to capture all traffic in an unencrypted format. You can find out more about Ettercap in our Ettercap Cheat Sheet.
8. Foremost
Foremost operates at the command line and it performs data recovery functions. Foremost works on disks that might have been damaged, losing the FAT and scattering the links between segments containing parts of files. It is able to reassemble those fragments back into accessible files.
This utility was created by agents of the US Air Force Office of Special Investigations and it is used by law enforcement agencies around the world for recovering deleted or damaged files, including images. It is also used for copying entire disks for later analysis.
9. Hashcat
Hashcat is a command-line utility that focuses on system passwords. It is able to crack passwords or, as the creators express it, to recover passwords. As its name implies, the system works on hashing algorithms. Many systems store passwords in a scrambled state; Hashcat tries to work out which algorithm was used for that protection and then tries to reverse it to reveal the passwords in plain text.
10. Hydra
Hydra, which is also known as THC Hydra, is a password cracker. Hydra works at the command line and it is notable for the speed of its password attacks. This is achieved by running several attempts simultaneously.
The parallel operations of Hydra enable hackers and pen-testers to quickly cycle through a long list of possible authentication protocols until it works out exactly which system to use. It then performs a range of attack strategies to discover username and password combinations.
11. John the Ripper
John the Ripper is another password cracker. This also detects the hashing algorithm in use and then tries to decrypt the password file. The John the Ripper package includes a range of password cracking tools, including brute force password guessing. You can choose to generate a password dictionary to try or import one from another tool. It is also possible to create your own dictionary to use for password guessing attempts.
12. Kismet
Kismet is a packet sniffer that can be used to explore a network. Where this tool is different from most network discovery tools, it works on wireless networks. Kismet has a great user interface that features live signal strength indicators for each channel.
By identifying all channels, the system can capture traffic in a conversation. By examining the contents of transmission to discover new devices with their identities and user accounts. Kismet can also be used as an intrusion detection system.
13. Maltego
Maltego is an unusual tool and can be very powerful. It constructs relationships between information points. The first task of the system is to discover devices, scan them, and document the software and settings of each. It then creates a map of these dependencies.
The Maltego mapping system can also be applied to user accounts and hierarchies. One of the most powerful capabilities of Maltego is its ability to map social media accounts and the connections between them. Maltego’s crawling can be limited to a specific network or allowed to chain out all over the world, passing through a range of systems.
14. Metasploit Framework
Metasploit is a well-known hacker tool that is owned and developed by the cybersecurity firm, Rapid7. There are two versions of Metasploit. The edition that is bundled into Kali, Metasploit Framework, is free. The higher version is a paid tool, called Metasploit Pro.
The main purpose of Metasploit Framework is a vulnerability scanner. After a system sweep to discover exploits, Metasploit offers an interface in which to compose attacks.
15. Nikto
Nikto is a web vulnerability scanner that runs at the command line. The tool looks for 6,700 dangerous programs and also scans services, such as Web server and email server systems – it includes scans for a total of 1,250 server versions.
After identifying all of the software on a Web server and categorizing it as threatening, weak, or worthwhile, the system then checks through all of the settings of those systems. The Nikto system can be used to protect a system by testing intrusion detection systems.
16. Nmap
Nmap, also called Network Mapper is a highly respected network discovery tool. This is a command-line tool that can also be run through scripts. For a GUI version, you should access Zenmap, which is also included with Kali Linux.
Nmap operates as a packet sniffer. It looks into the headers of passing traffic to log all of the different devices and the applications operating on each that generate traffic.
The facilities of Nmap are designed to run within a network. It can be used by network administrators or consultants who want to quickly document a network. It is also a very useful tool for white hat hackers.
17. OWASP ZAP
OWASP is the Open Web Application Security Project. One of the key products of OWASP is the Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP). The service is centered on a traffic interceptor that focuses on Web transactions. This system has a graphical user interface, which makes it easy to use.
Tools within the ZAP system include a web crawler, a URL fuzzer, and a vulnerability scanner. These systems operate through a proxy server, which acts as a collection point for vulnerability data. These processes test the security services of a network and the Web server itself.
18. sqlmap
Sqlmap is a command-line utility that offers a number of different ways to probe the security surrounding databases that work as services to websites and networked services, such as ERPs.
The implementation of sqlmap is formed through one command, which can be modified by a very large number of options. Every run of this program performs a scan on a database that is accessed through a specific URL or a local address. The standard scan will identify the DBMS and then try to attack it with a range of SQL injection strategies.
The sqlmap system can be used to document databases, crack credentials, and extract data. We examine this tool in greater detail in the sqlmap Cheat Sheet.
19. Wireshark
Wireshark is a very widely-used packet sniffer and you probably already use it. This system is able to extract passing network packets on LANs and wireless networks – even Bluetooth. The service provides a GUI interface and there is also a command-line version called TShark.
You probably won’t use Wireshark exclusively but it is likely to be your top choice for a packet sniffer among all of the alternatives included in the Kali Linux bundle. This system is able to exchange data with system management tools and analysis utilities, so it will form the data feed for many other applications in your armory.
20. WPScan
WordPress is very widely implemented and is the most popular content management system in the world. The service has its own environment, which can make it difficult for security tools to fully explore a WordPress-based website for vulnerabilities. WPScan specializes in uncovering vulnerabilities within WordPress implementations.
The free version of WPScan, which is integrated into Kali Linux is a command-line system. This makes it a little harder to use for non-technical website owners. However, it is worth putting in the time to learn how to use this vulnerability scanner because it searches for more than 23,000 WP-specific exploits.
Kali Linux FAQs
Is Kali Linux OK for beginners?
Kali Linux isn’t designed as a tool for beginners. The core of the tool is the Linux operating system, so you need to know the Linux command set first of all. Many of the tools included in the Kali Linux package are command-line systems and require a lot of studying to use because they are not as user-friendly as applications that have a GUI interface.
Which is better Ubuntu or Kali?
Ubuntu and Kali are two versions of Linux and both are derivatives of Debian. Kali has much more than Ubuntu because it comes packaged with a long list of cybersecurity tools. If you don’t need those security tools, all of the features of Kali would be a waste of space on your computer, so you would be better off with Ubuntu.
Is Kali Linux harmful?
Kali Linux is not illegal. The bundle of tools included with it are meant for use by penetration testers. The purpose of penetration testing is to use the methods deployed by hackers in order to test the security of an IT system. In order to provide the systems needed for penetration testing, Kali Linux includes many of the tools used by hackers. So, the package could be put to harmful use.